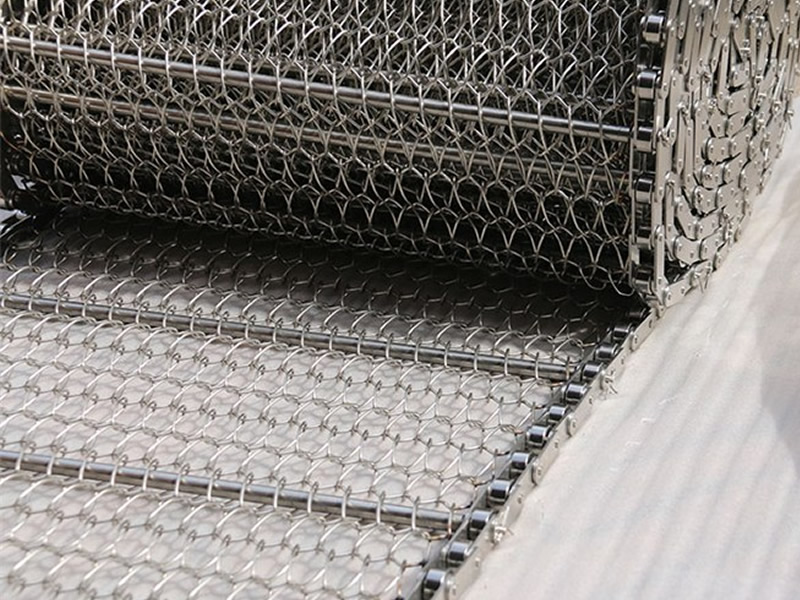
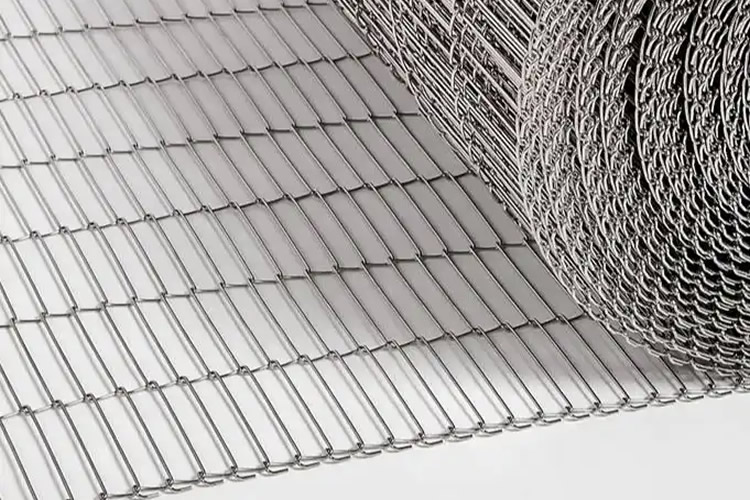
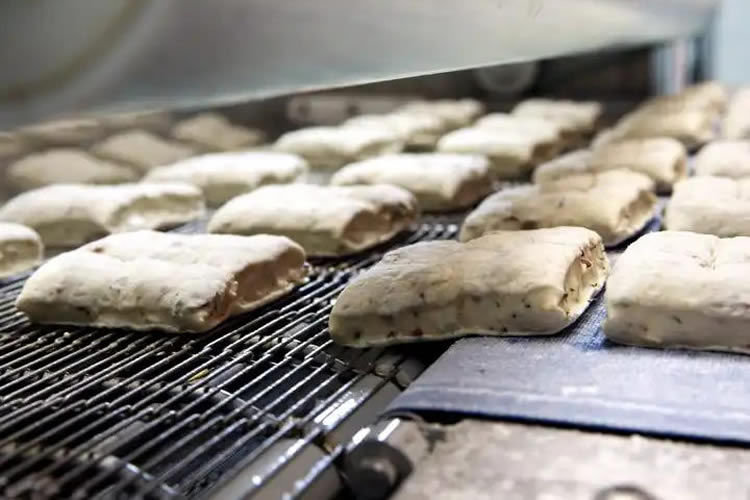
Wire conveyor belts are versatile conveyance systems made from interlinked metal wires, forming a sturdy and open mesh pattern. These belts are designed to facilitate the transport and processing of goods across various industrial settings. Due to their metal construction, they are particularly suited to environments that require durability, heat resistance, or exposure to harsh chemicals.
Material
- Stainless Steel: Perfect for hot, wet, or dirty places. Rust-resistant.
- Carbon Steel: Very strong for hard tasks but can rust without proper care.
- Galvanized Steel: Like carbon steel but with rust protection. Cost-effective.
- High-Carbon Steel: Stronger than regular, for very demanding work.
- Nickel Alloys: Extremely durable, great for extreme heat and no rust.
Specifications
- Sizes and Performance
Widths Available: From 200 mm to 5,000 mm, with options up to 160 inches for larger needs.
Speed: Can go up to 1000 feet per minute.
Temperature: Handles up to 2100°F, depending on the belt material. - Durability
Edges: Reinforced with knuckled edges for longer wear. - Wire and Rod Details
Wire Diameter: Ranges from 1.2 mm to 3 mm.
Cross Wire Diameter: From 1.2 mm to 4.0 mm for added strength.
Flat Wire Size: Between 1.0 mm × 0.7 mm and 6.0 mm × 3.0 mm for various contact needs.
Spiral Wire Pitch: Selections from 4 mm to 22 mm to adjust mesh tightness.
Cross Rod Pitch: Wide range from 4 mm to 33 mm, with many increments like 5, 6, 8, 10, etc., for specific applications.
Spiral Wire Diameter: From 0.9 mm to 3.0 mm for handling different loads.
Classification
- Flat Wire Conveyor Belts: Perfect for small parts and requiring a stable surface. Used a lot in food processing and electronics for its toughness and easy cleaning.
- Balanced Weave Conveyor Belts: Great for tension and flexibility, these belts are best for high-temperature uses in the food industry, like ovens and fryers.
- Rod Reinforced Conveyor Belts: Built for strength and durability, ideal for heavy loads and stable, minimal-stretch applications, often seen in heat treatment.
- Chain Link Conveyor Belts: Simple, flexible, and great for moving items straight, especially in bottling and packaging.
- Spiral Conveyor Belts: Designed for spiral cooling/freezing, offering uniform cooling with high airflow, perfect for bakery and frozen foods in the food industry.
- Plate Link Conveyor Belts: Strong, with plates or slats for heavy loads at slow to medium speeds, mainly used in metalworking and recycling for its durability.
- Wire Loop Conveyor Belt: Flexible with high airflow, making it great for gentle product handling, like cooling bread and pastries.
- Honeycomb Conveyor Belts (Flat Wire): Strong and stable, excellent for environments needing stability and airflow, like baking and cooling in food processing.
- Eye-Flex Conveyor Belts: Heavy-duty for high loads and tough conditions, suitable for moving heavy items like auto parts and scrap metal in industrial settings.
Wire Conveyor Belt Edge Types
- Welded Edges: Edges are melted together for a smooth finish, making the belt strong and less likely to snag or unravel. Great for belts that need to be extra durable.
- Clinched Edges: Edges are folded over and flattened, avoiding sharp points. This makes the belt safer, especially where it’s important to protect the products being moved.
- Chain Edges: A chain is added along the edges, matching the belt’s material. This strengthens the edges and helps keep the belt on track, especially useful for heavy-duty jobs.
- Reinforced Edges: Extra wire or thicker material boosts edge strength, helping the belt carry heavy loads without wearing out the sides.
- Special Coatings or Coverings: Edges can be coated or covered with materials like rubber to prevent wear or corrosion, or to meet health standards in food and pharmaceutical industries.
- Choosing the right edge treatment helps the belt last longer, perform better, and operate safely in its specific environment.